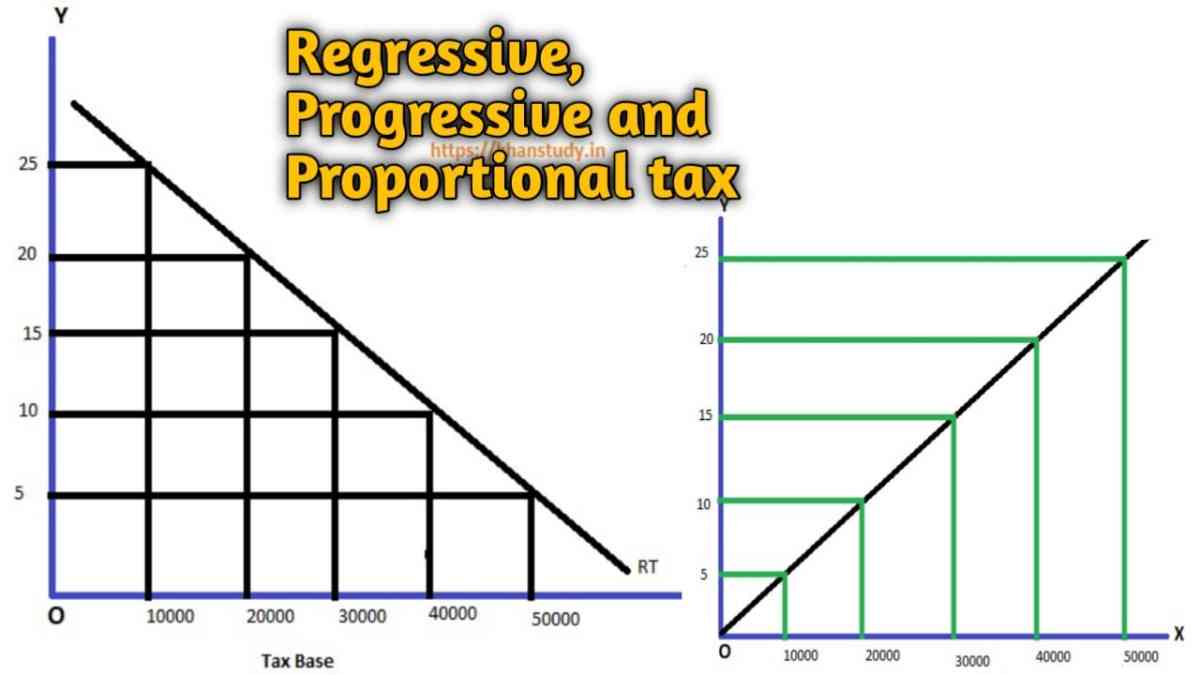
The tax is imposed on the basis of income. Therefore, a tax may be proportional, progressive and regressive according to the relationship between its rate structure and the income, wealth or economic power of the tax payers. In today’s article we are going to know about Progressive tax, Regressive and Proportional tax (Note on Taxation System). So let’s discuss this.
Table of Contents
What is Progressive tax or taxation?
A progressive tax is that in which the rate of the tax depends on change in the income of the individual. It implies that the rate of taxation should increase with the increase in income. Thus higher the income, the higher should be rate of taxation.
The progressive taxation can be explained with the help of an example- (Progressive tax example)
| Tax balance (Income) | Tax rate (%) | Amount of tax |
| 10,000 | 5% | 500 |
| 20,000 | 10% | 2000 |
| 30,000 | 25% | 4500 |
| 40,000 | 20% | 8000 |
| 50,000 | 25% | 12500 |
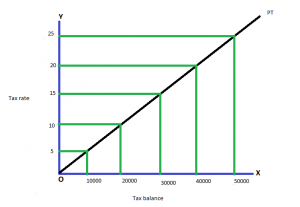
Merits of Progressive tax
• Progressive tax follows the canon of equity.
• In the UDCs (Under develop countries) progressive tax acts as a powerful tool for reducing income inequalities.
• Progressive taxes are economical because the cost of collection is very low.
• It is suitable because the govt. revenue automatically increase with the increase in economic activity (More Productive).
• Progressive taxation may be helpful to check the inflationary pressure as it reduce consumption demand. Thus it promotes stability in the economy.
Demerits of Progressive tax
• Progressive tax system is very complex to understand.
• Progressive tax affects the capital formation process of the economy.
• This tax system encourage evasion.
• It is claimed by the critics that in reality. Progressive taxation hampers social welfare as it is a subjective.
• It is argued that it is based on wrong assumption of marginal utility of money which is loss to a rich person as compared to poor person.
What is Regressive tax or Taxation System?
A regressive tax is that in which the rate of tax depends on the income of an individual. It implies that the rate of taxation decreases with the increase in income. Thus higher the income, the lower is the rate of taxation.
The regressive taxation can be explained with the help of an example- (Regressive tax example)
| Tax base (Income) | Tax rate (%) | Amount of Tax |
| 10,000 | 25% | 2500 |
| 20,000 | 20% | 4000 |
| 30,000 | 15% | 45000 |
| 40,000 | 10% | 4000 |
| 50,000 | 5% | 2500 |
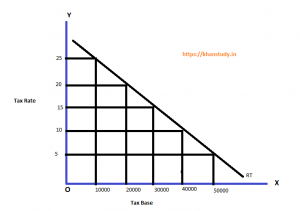
Regressive tax system is a simple form of the tax structure. But this taxation is against the objective of a welfare state. Because this tax provides more pressure on the lower income group. This it breaks the principle of equity. For this reason the government does not follow the regressive tax structure.
Merits of Regressive Taxation
• Regressive tax is imposed on the persons. So that consumption of unwanted goods may be reduce. In this way regressive tax have public utility.
• Regressive tax is more useful when the use of intoxicant goods increased by the poor.
Demerits of Regressive Taxation
• It has been observed that regressive tax has an adverse effects on savings and capital formation in the country.
• Another disadvantage of regressive tax is that there is more possibility of tax evasion.
• The imposition of more taxes an poor is not logical.
What is Proportional Tax system?
A proportional tax system is that in which the rate of tax depends on the income of an individual. It implies that the rate of taxation should remain constant with the increase in income. Thus, higher the income the rate of taxation is same.
The proportional taxation can be explained with the help of an example- (Proportional tax example)
| Tax base (Income) | Tax rate (%) | Amount of Tax |
| 10,000 | 10% | 1000 |
| 20,000 | 10% | 2000 |
| 30,000 | 10% | 3000 |
| 40,000 | 10% | 4000 |
| 50,000 | 10% | 5000 |
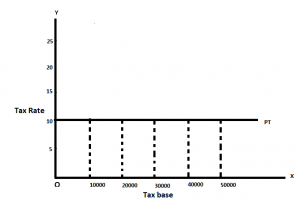
Merits of Proportional Tax or taxation
• The evaluation of the total tax under this tax system is quite simple and quick.
• It is more uniform than the progressive taxation.
• It brings no change in the existing distribution of income and wealth.
• It does not adversely affect the people’s desire to work.
• As the rate of tax does not change with the change in income, it is easy to calculate.
Demerits of Proportional Tax System
• The proportional tax system does not lead to equitable and just distribution of the burden of taxation.
• It is not according to the ability to pay of the individual low income group tail to pay the heavy burden of taxation.
• This system is not elastic as the financial needs of a govt. may change from time to time.
• It does not go parallel to principle of taxation capacity.
Conclusion
So friends, this was Progressive tax, Regressive and Proportional tax (Note on Taxation System). Hope you get the full details about it and hope you like this article.
If you like this article, share it with your friends and turn on the website Bell icon, so don’t miss any articles in the near future. Because we are bringing you such helpful articles every day. If you have any doubt about this article, you can comment us. Thank You!
Read More Article
• Economic thoughts of Mahatma Gandhi | Discuss the ideas of M.K Gandhi