Hi friends, in today’s article we are going to know about the theory of optimum tariff with suitable diagram. So let’s discuss in details.
Table of Contents
Theory of Optimum Tariff
The imposition of tariff always raises the gain for the tariff imposing home country in the form of the improvement in the terms of trade. At the same time, tariff involves cost the form of reduction in the volume of export & imports.
So long as the gain from tariffs is more than the cost of it, the welfare of the tariff imposing country increases and it is worthwhile for it to raise tariff. In case the cost of tariff for the society is more than the gain from tariff.
There may be reduction in the level of economic welfare and worsening the terms of trade. In such a situation, it is appropriate to reduce tariff.
The level of tariff which does not further increase the benefit to the given country and the level of economic welfare becomes maximum, is known as the optimum tariff. According to Bo soderston, ‘the tariff that maximizes a country’s welfare is called the optimum tariff.
What is Optimum Tariff diagram?
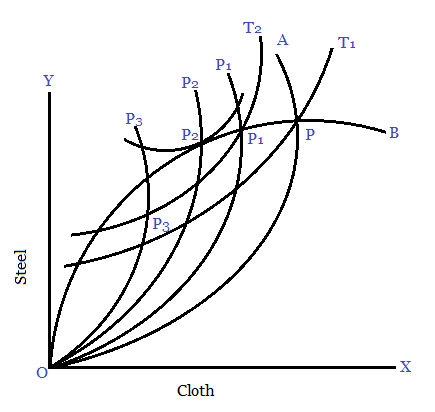
The level of optimum tariff can be explained with the help offer curves and trade indifference curve (IC). The point of optimum tariff is determined where the trade indifference curve of the tariff imposing home country becomes tangent to the offer curve of the foreign country.
Thus in following diagram OA is the offer curve of home country A and OB is the offer curve of foreign country B. T1T2 and T3 are the trade indifference curve of country A.
Before the imposition of tariff, the exchange takes place at P. This point lies on the trade indifference curve T₁. As tariff is imposed the offer curve of country A shift to OA1 and exchange tale place at P₁. This point occurs at the higher trade indifference curve T2.
Thus tariff results in an improvement in terms of trade on the one hand and increases the level of welfare on the other. If there is a further increase in tariff country A’s offer curve shift to OA2 and given the offer curve OB of country B, the exchange takes place at P2.
This point occurs at the higher trade indifference curve T3 and foreign country B’s offer curve OB. Compare with point P1, there is a further improvement in the terms of trade and increase also the level of welfare.
In such a situation it is appropriate for the home country to reduce tariff and move back to the point P2 where the welfare is maximum. Thus P2 is the point of optimum tariff which corresponds with the maximization of welfare.
Conclusion
So friends, this was the concept of optimum tariff. Hope you get the full details about it and hope you like this article.
If you like this article, share it with your friends and turn on the website Bell icon, so don’t miss any articles in the near future. Because we are bringing you such helpful articles every day. If you have any doubt about this article, you can comment us. Thank You!
Read More Article
• Capital Accumulation | What is Capital Accumulation in Economics?
• Non Bank Financial Intermediaries | Bank and Non bank financial intermediaries